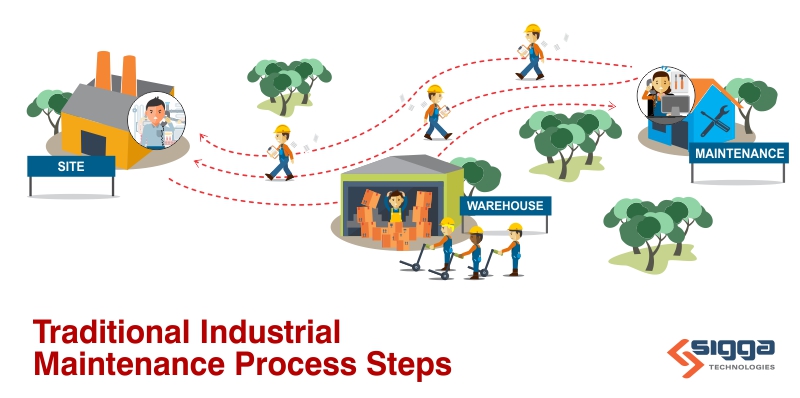
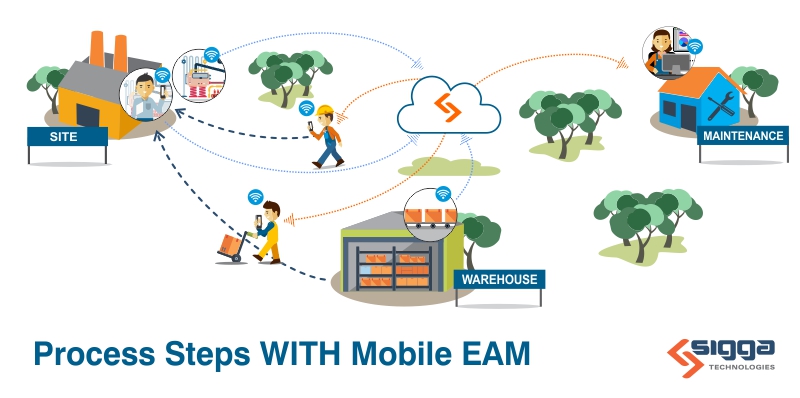
SAP Plant Maintenance(PM) plans are key to reducing and minimizing the impact of unplanned events on safety, the environment, and business profitability. But creating and staying committed to the execution of PM plans is often a challenge with limited resources and data quality issues.
In this article, we will discuss how organizations can improve data collection and analysis to make informed decisions and improve preventive maintenance plans.
Making a Commitment to Increase Preventive Maintenance
When Equipment is not working properly,it is not producing capacity. A lack of production translates to lost revenue. Worse still, complete failure can result in significant costs to repair or replace equipment,idle production staff,and even loss of raw materials such as spoilage in food & beverage manufacturing. Preventive Maintenance goes a long way towards maximizing productivity and avoiding costly unplanned downtime.
Many organizations do not effectively deploy proactive maintenance strategies such as preventive, predictive,and reliability-centered maintenance. As the Marshall Institute notes, there is a heavy tendency to use the approach of “run to failure” rather than practicing preventative maintenance. And even in maintenance departments that indicate that they are committed to preventive maintenance,many do not practice it fully or effectively.
One of the reasons that these initiatives often fail is that the preventive maintenance (PM) plans are not based on the right data. Maintenance planners rely on a broad range of data sources when putting together PMtasks. For example, equipment manufacturers’ manuals, work order history,and advice from reliability experts. Since many maintenance organizations continue to rely on paper-based processes and manually input data into SAP,PM tasks are often based on incomplete and inaccurate data. Thus,data integrity plays a crucial role in creating and implementingPM plans.
Data Integrity in SAP Plant Maintenance
Maintenance leaders are often surprised to learn that even though they have powerful system to manage maintenance data in SAP PM, they may not be getting the most out of it. Such was the case in a South African-based petrochemical plant. Management began to notice that PM jobs and repairs were not being completed on their first attempt. This contributed to an increase in the work backlog, rising costs, and inefficient use of maintenance technician’s time.
As management delved further into the issue, they identified something that was both troubling and astonishing.Since Work order results were manually entered into SAP, the details on what happened and the cause of the failures were based on hand written notes. In SAP PM, these are open text fields to capture the data.As they looked into the data, they found over 300 different reason code for failure that pointed to one issue: the parts were not available to complete the work order the first time.
The open-ended responses created a database that could not be easily analyzed by stakeholders to look at failures,root causes,nor trends. A lack of standard data entry fields negatively impacted the data integrity. And poor data integrity leads to incomplete and/or ineffective maintenance planning.
Developing an Effective SAP Preventive Maintenance Plan
Failure analysis is a crucial component of a proactive maintenance culture. It involves collecting and analyzing failure data to identify the root cause of a breakdown. Failure analysis typically conducted after a failure has already occurred.Reliability engineer and maintenance managers can use what they learn to improve the planning of PM tasks as well as modify machine design or how equipment is used.
But failure analysis is only useful in the maintenance planning process if stakeholders have access to complete and accurate data. This means streamlining and standardizing the collection of maintenance data within SAPPM through the use of automation technologies. For example, through the use of mobile EAM solution technicians can identify the reasons for failure using drop-down menus of predefined reason codes. This information is automatically synced with SAP to give maintenance planners the reliable and complete data they need tocreatePM plans.
While the process of improving SAP PM plan may seem overwhelming, you can get started by following the steps outlined here:
- Audit Data Resource
The first step is to compile your data resources to ensure that you will have the data that you need to engage in meaningful analysis.Then determine which assets you want to include in your preventive maintenance plans. For organizations that do not have established preventive maintenance processes, you may only want to start with a handful of your most important assets and scale up from there.
Relevant data resources will include things like manufacturer repair manuals,pastwork orders, and failure reports.If your maintenance department relies on paper-based work order management and SAP PM,this will be a time-consuming task until you better structure the data inputs into the system.Focus on pulling together the data from past work orders for each assetto determine:
- What failed
- When it failed
- Why it failed
- What Type of repair was done
- Did it fail again
- Conduct RCA and/or FMEA
Effective Maintenance planning encompasses two perspectives: what did happen and what could happen. RootCauseAnalysis (RCA), also called failure analysis, looks back at what has already happened. When you experience a corrective or breakdown event, an RCA involves looking at why the problem occurred and working your way down until you identify the underlying causes. For each cause, you can identify a solution. These solutionscanbecometasks in your PMplan.
Unlike RCA,Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)seeks to identify what could happen by identifying potential failure modes (FM).There are several types of FMEA analysis: Design, Process and Functional. We are going to focus onFunctional examples.The process starts with a bottoms-up approach. Each component of an asset is examined to identify all potentialFMsthat can happen and what would be the consequences of each failure. Since technicians are the most familiar with assets, they are typically the best resource for identifying these details.
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis – Pump System Example
| Equipment function |
Functional failure |
Component |
Potential failure modes |
Potential effects of failure |
Potential causes of failure |
Current controls |
Frequency Of controls |
| Provide process flow |
Loss of process flow |
Motor |
Seized bearings |
Total loss of capacity |
Lack of lubrication |
Lube motor bearings |
6M |
| Provide process flow |
Degraded process flow |
Impeller |
Reduced discharge pressure |
Partial loss of capacity |
Normal wear |
Overhaul pump |
2Y |
Making FMEA the heart of an equipment maintenance plan
- Prioritizing Risks
Using this information, maintenance department scan then set criteria for evaluating the level of risk of each identified failure and assignita Risk Priority Number (RPN). The RPN is a metric that used to prioritize maintenance tasks based the likelihood of an occurrence,ability to detect the problem, and the severity of the impact.For example– rating the severity(SEV)of the failure:
| Rating |
Effect |
Severity of the effect |
| 10 |
Hazardous without warning |
Very high severity, potential effects safe system operation without warning |
| 9 |
Hazardous with warning |
Very high severity, potential FM effects safe system operation with warning |
| 8 |
Very high |
System inoperable with destructive failure without compromising safety |
| 7 |
High |
System inoperable with equipment damage |
| 6 |
Moderate |
System inoperable with minor damage |
| 5 |
Low |
System inoperable without damage |
| 4 |
Very low |
System operable with significant degradation of performance |
| 3 |
Minor |
System operable with some degradation of performance |
| 2 |
Very minor |
System operable with minimal interference |
| 1 |
None |
No effect |
Source: Failure Mode and Effects Analysis Under Uncertainty: A Literature Review and Tutorial
Follow the same approach to identify a scale for likelihood to occur(OCC) and likelihood of detection (DET) and multiply the three risk factors to determine a RPN number.Then, working with the engineers and technicians identify recommended actions, frequency required, and forecast the end result using the sameRPN scale.
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis – Pump System ExampleContinued
| Risk assessment (as is) |
Recommended improvements/actions |
Recommended improvement process frequency |
Responsibility/ date |
Risk assessment (to be) |
| SEV |
OCC |
DET |
RPN |
|
|
|
SEV |
OCC |
DET |
RPN |
| 6 |
5 |
3 |
90 |
Include on vibration and IR route |
3M |
PdMTech/ 1Q22 |
6 |
3 |
2 |
36 |
| 4 |
6 |
5 |
120 |
Monitor flow and discharge pressure |
1W |
Operation/ 1W22 |
4 |
6 |
3 |
72 |
Making FMEA the heart of an equipment maintenance plan
This type of analysis can start at a high-level,looking at the major components of a critical asset, then overtime go deeper into sub-components and materials.
The result allows maintenance engineers and managers to prioritize PM tasks and make informed decisions to improve the organization’s commitment to executingPM plans.Redo The analysis annually to evaluate the impact and further refine your plans for further optimization of your resources.
In Conclusion
Preventive Maintenance help organizations avoid unplanned downtime and improve resource allocation.While many organizations indicate that they are committed to preventive maintenance plans, initiatives are often hampered by the lack of quality data and the ability to analyze it.
Start with structuring the capture of data for analysis and then you can look at industry-proven methods like RCA and/or FMEA to prioritize and focus yourPM plans.Understanding the RPNpriorityof a planned task improves the organization’s commitment to see that it is performed on time. Plus,based on data, you can optimize the frequency of a task– possibly reducing the number of PMs required per year,more efficiently utilize your resources, and increase your schedule compliance.
By making the commitment to better capture and structure data,analyze failures,and build better SAP Plant Maintenance plans, you can achieve long-term results with higher asset OEE and minimize the impact of unplanned events on safety, the environment,and business profitability.
How Sigga Can Help
Sigga is a certified SAP partner with over two decades of experience providing industry-leading industrial maintenance solutions. Our mobile EAMsolution streamlines the collection of data. Work orders are dispatched to technicians on their mobile devices. Technicians automatically capture and structure the data needed for analysis through their day-to-day use of the app to complete their work orders.Data is automatically synced with SAP Plant Maintenance. This solution solves data gaps and helps enable maintenance teams to be able to create, implement, and monitor preventive maintenance plans.
In addition, our planning and scheduling solution automates routines to improve the deployment of preventive maintenance programs with full visibility to the prioritization of tasks.With these two solutions, our clients have seen productivity results from 15% to over 50%.
Sigga Solutions
Read more about Sigga Solutions and how we can help you improve your preventive maintenance program.