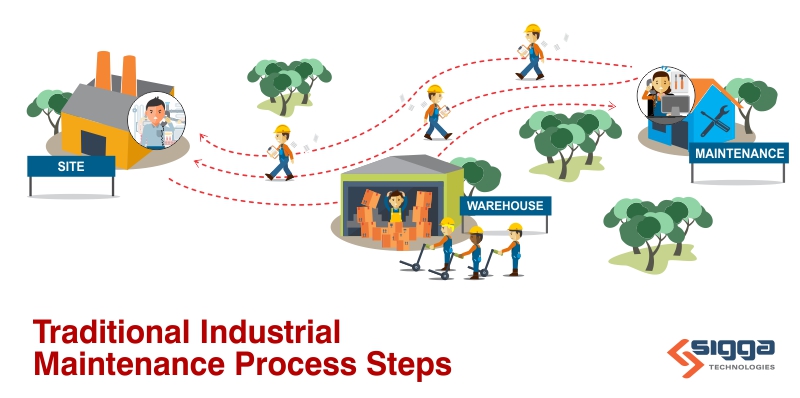
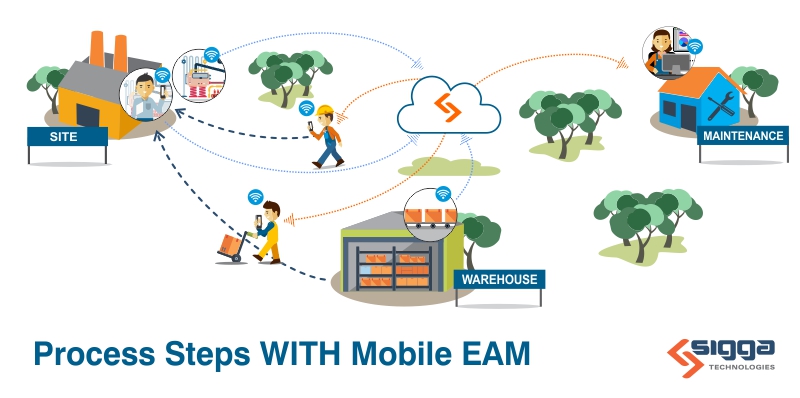
A checklist can help ensure any task, no matter how simple or complicated, is completed properly. From shopping lists to preventive maintenance procedures, checklists document the items needed to be completed and serve as a guide for the person completing the task.
This article will explain the benefits of creating preventive maintenance checklists and provide eight tips to make sure they are effective.
Why are Preventive Maintenance Checklists Important?
Without a preventive maintenance checklist, technicians must rely on equipment manuals which can be bulky, hard to read and even hard to find. Preventive maintenance checklists standardize the process, so the same steps are taken no matter who is completing the task. Preventive maintenance checklists also increase productivity and safety, while allowing for faster troubleshooting and better planning.
Preventive maintenance checklists can also help companies meet safety and compliance requirements. In industries that are evaluated by regulators, like food production, maintenance checklists can be used to provide a record of completed inspections to auditors.
Most importantly, preventive maintenance checklists help avoid unplanned industrial maintenance. Unplanned maintenance requires technicians to spend more time on the repair due to the need to diagnose the problem, as well as obtain parts and repair instructions. It can also lead to more overtime costs. Indirect impacts include unplanned production downtime, late orders, and customer satisfaction issues.
Tip 1: Organize Resource Materials
Before getting started actually creating preventive maintenance checklists, it’s key to get organized. The first step is to determine which assets actually need checklists. If you have a small number of assets this might not be necessary but can be very useful if dealing with a large number of assets.
Next, collect the operating manuals and equipment documentation for the selected assets. Make sure you also have the latest safety and compliance requirements handy. Lastly, be sure to check past asset performance. Being aware of equipment that fails often can help you outline additional maintenance that may be needed in addition to what the equipment manufacturer recommends.
Tip 2: Choose the Proper Type of Checklist for Each Asset
Once you are organized, you’ll need to decide what type of checklist to create for each asset. Two common types of preventive maintenance checklists are pass/fail and step-by-step. Let’s look at the uses for and examples of each.
Pass/fail Checklists
Simple pass/fail checklists are often used for equipment inspections where technicians are looking for early signs of trouble. Pass/fail checklists can be used to monitor ideal equipment conditions, such as temperature, water pressure, or oil level on a regular basis. For example, a pass/fail checklist could direct technicians to check the oil to ensure it is at an acceptable level. If the oil level is satisfactory, the equipment passes. If not, it fails. In this case, a condition fail could trigger a notification to add more oil to the machine. In other cases, a condition fails, like increased temperature, could be indicative of an impending failure.
Example Pass/Fail Checklist:
| Component |
Yes |
No |
N/A |
Defect |
| Electric Lift |
| Does it turn on/off? |
|
|
|
|
| Is there abnormal noise? |
|
|
|
|
| Does it go up and down? |
|
|
|
|
| Emergency release: Does it work? |
|
|
|
|
| Hand control: Do all the buttons work? Are the electrical wires frayed? |
|
|
|
|
| Bolts on lift. Are they fastened tightly? |
|
|
|
|
| Weld sites. Are there any cracks? |
|
|
|
|
Step-by-Step
On the other hand, step-by-step checklists are often used for tasks that are more involved than just monitoring equipment conditions. Step-by-step checklists should be used for more complex preventive maintenance procedures like changing belts, motors, or other parts of the equipment. The step-by-step checklist details the instructions for completing each step of the task from start to finish. Step-by-step checklists ensure that the same process is followed by each technician and all important steps are completed.
Example Step by Step Checklist:
|
|
Component
|
Jan
|
Feb
|
Mar
|
Apr
|
May
|
Jun
|
| Evaporative Condenser |
| 1 |
Check condition of drive B-belts. Replace if necessary. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
Check operation of low water float. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 3 |
Check operation of condenser pan water heater and thermostat. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 4 |
Check ball valve for correct operation, lubricate arm and set for correct water level. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 5 |
Check and lubricate fan shaft bearings and locking collars. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 6 |
Check operation of fan motor. Grease adjusting screw. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 7 |
Check/adjust condenser drives if necessary. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tip 3: Select the Recommended Frequency for Each Checklist
Not all checklists will need to be completed with the same frequency, so you should decide how often each checklist should be utilized.
- Daily preventive maintenance checklists are often used for inspections like checking the temperature on a machine or conducting safety checks between shifts.
- Weekly checklists are often used for inspections that don’t need to be completed as frequently as a daily inspection. They may also include a task related to a daily checklist. For example, a daily task may be to check the water level in a machine, the weekly task might be to add water.
- Monthly preventive maintenance checklists likely include even more tasks related to the weekly and daily checklists, like emptying and replacing the water in a machine.
- Quarterly checklists are often related to inspections by third parties to make sure equipment is meeting safety or industry standards.
- Seasonal preventive maintenance checklists are often related to changes needed for different weather conditions, like winterizing equipment or switching the HVAC systems from cooling to heating.
- Annual checklists are usually comprised of more complex tasks such as disassembling a machine to make sure all internal components are functioning properly.
Tip 4: Ensure Checklists are Clear and Succinct
Preventive maintenance checklists need to be carefully crafted to provide clear instructions that even a new technician can follow. Assuming the technician knows what do to and providing too little information can prevent the task from being completed properly. On the flip side, too much information may be overwhelming, cause confusion, and slow down the maintenance process.
Preventive maintenance checklists should include all the essential details needed to complete the task but be written as succinctly as possible. Break down long descriptions or processes into multiple, shorter steps. Make sure each step describes an actionable item or remove it from the checklist. After drafting the checklist, review it to ensure all steps are in the proper order.
Tip 5: Ensure Checklists Include All Needed Information
Not only should checklists be written clearly in steps that are easy to understand, but they also need to include all the information a technician will need to complete the job. Preventivemaintenance should include a comprehensive list of tools and parts needed to complete the work.
Remember to include any important safety information such as personal protective equipment (PPE) required and lockout, tag out (LOTO) instructions to ensure the machine cannot be started while maintenance is in process.
Preventive maintenance checklists should also contain the approximate time each task will take, as well as the total time for completing the work. Be sure to include visual aids like photos, videos, and diagrams if appropriate.
Tip 6: Get Input from Several Perspectives
Once you have completed your preventive maintenance checklists, you should seek input from other parties to ensure the lists are understandable and include all necessary steps. Checklists should be reviewed by maintenance planners, maintenance operations, and senior technicians to identify any gaps. Be sure to also consult with production operations, as in many cases, they are the people actually doing the inspections or maintenance procedures from the checklists.
Tip 7: Review Checklists Regularly
After checklists have been finalized, it’s important to review them regularly to make sure they are achieving the goal of detecting problems. Make sure checklists aren’t missing any key steps that could potentially identify an issue. Likewise, ensure that checklists don’t include directions to perform activities that have no impact on identifying or preventing problems. If an asset breaks down immediately after being serviced, the checklist should be reviewed to ensure all necessary maintenance steps were included and that nothing else could have been done to prevent the failure.
Tip 8: Use Software Tools to Make the Job Easier
Utilizing software tools to create preventive maintenance checklists makes the job easier and more efficient. These tools, which can integrate with your SAP Plant Maintenance system can further automate preventive maintenance routines.
Providing a mobile application for technicians and inspectors can improve the access and use of the checklists, plus record results which is especially important to demonstrate compliance with industry regulations. Mobile preventive maintenance checklists can be created and require confirmation of the completion of each step before confirming the completion of the checklist. The details are then stored in SAP for compliance reporting.
Lastly, mobile maintenance apps support the collection and analysis of data on failures to support the continued improvement of preventive maintenance checklists.
| Inspection Compliance at a Global Food & Beverage CompanyA Sigga customer required inspections that could include over 100 operations per each piece of equipment. When we first met with the company, they were managing the process on paper with hours spent every week to update each operation individually in SAP with an “ok” or “not ok”. The data entry process often took longer than the inspection itself!
We helped the company implement a mobile maintenance solution and create checklists that could be completed by the inspector and updated in mass to SAP completely cutting out the manual data entry process. For “not ok” operations, a new notification was automatically created in SAP copying the inspection order and text entered by the technician detailing the problem. This process was a quick “customization” to Sigga’s EAM Empower app utilizing our unique no-code software platform.
As you might imagine, the time savings for the organization are significant. In addition, they were able to improve their compliance reporting. |
Benefits of Effective Preventive Maintenance Checklists
Effective preventive maintenance checklists allow you to utilize data to turn your maintenance processes from slow and error-prone to efficient and proactive. Checklists can help you fine-tune and improve maintenance schedules, as well as help you make changes quickly if an emergency occurs.
Preventive maintenance checklists can also help you improve maintenance effectiveness ratios and the bottom line. In a presentation entitled “The New Approach to Plant Maintenance,” ABB Reliability Services suggested that one hour of properly performed planned maintenance avoids three hours of repair work. Other industry experts estimate that unplanned maintenance can cost 3X to 9X more than planned maintenance.
Let Us Improve Your Preventive Maintenance Checklist Processes
Here at Sigga, we have been helping asset-intensive industries with SAP Plant Maintenance drive digital transformation and mobile initiatives in industrial maintenance for 20 years. Our SAP Certified EAM software solutions can help you improve the capture, structure, and quality of the data needed to build and execute effective preventive maintenance checklists.
Our EAM-Empower mobile EAM application digitizes the entire maintenance process connecting users across your business in real-time. It helps your technicians accurately capture the data you’ll need to create effective preventive maintenance checklists.
Using the mobile interface to SAP, technicians can capture inspection results in real-time. In workplaces without connectivity, technicians and inspectors have full access to all the information they need to complete a checklist while offline. The app then automatically syncs when they are back online without user disruption.
Plus, with our no-code platform, you can easily modify the app to meet your unique maintenance and inspection requirements.